IVDR Transitional Provisions – Something had to give!
On the 23 April 2024, the European Parliament unanimously approved the proposal to amend the EU MDR (2017/745) and IVDR (2017/746) regarding the gradual roll out of Eudamed, information obligation in case of interruption of supply and the transitional arrangements for certain in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDs).
The amendment has been requested by industry to ensure continued access to critical diagnostic products, essential for a smooth running European healthcare system, and offering a hight level of protection to patients and users of diagnostic tests.
Why was change needed?
The IVDR has applied for placing IVDs onto the EU market since 26 May 2022, replacing the existing IVD Directive 98/79/EC, this required that all devices, including legacy devices, must meet a higher level of regulatory compliance. In January 2022, the European Parliament and Council adopted an extension to the transitional arrangement, with extended timelines based on the risk classification of devices:
| Risk Class | Current deadlines for compliance |
| Class D (Highest Risk) | 26 May 2025 |
| Class C | 26 May 2026 |
| Class B, Class A Sterile | 26 May 2027 |
| New devices, Class A (Lowest Risk) | 26 May 2022 (No extension) |
| Devices used in Healthcare Institution | 26 May 2028 |
The original transitional extension was intended to ease the pressure on implementation issues and delay experienced with infrastructure (including Eudamed), Notified Body availability and manufacturing readiness, all of which were impacted by the Covid-19 outbreak.
While the transitions had allowed some breathing space, the industry is facing an uphill struggle to be ready to meet these dates.
What is changing?
- Further transitional extension for some devices
With the exception of legacy devices that do not require conformity assessment (Class A and devices used on Healthcare Institutions), additional time is being added to the transition time for IVDR, and existing devices can continue to be placed on the EU market until the following dates:
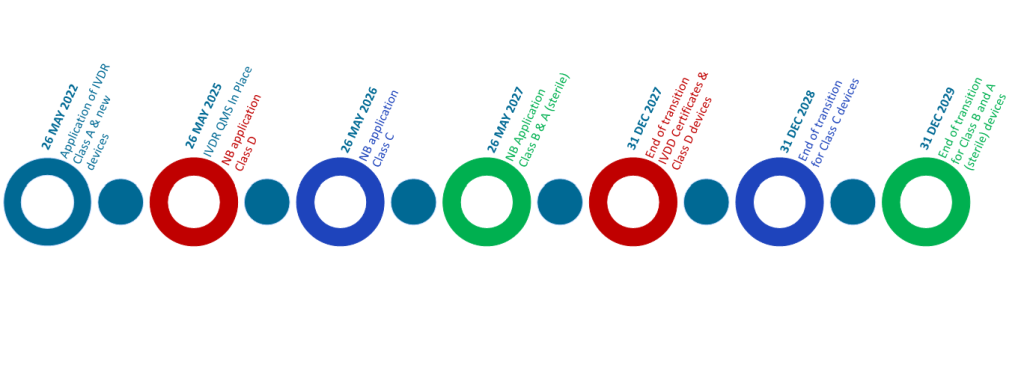
| Risk Class | Current deadlines for compliance |
| Class D | 31 December 2027 |
| Class C | 31 December 2028 |
| Class B, Class A Sterile | 31 December 2029 |
To use these timelines however, manufacturers must comply with certain conditions including:
- The devices are CE marked under the IVD Directive,
- There are no significant changes to the design or intended purpose,
- A Quality Management System compliant to IVDR shall be put in place by 26 May 2026,
- A formal application shall be lodged with a notified body 2 years prior to the dates above.
2. Bringing forward the mandatory use of Eudamed
The Eudamed database includes seven electronic elements including UDI, Vigilance and Market Surveillance. The earlier mandatory use of some Eudamed module would offer an enhanced adoption for this critical element of IVDR deployment.
3. Prior notice if supply of IVD is stopped
To reduce the risk of device shortages, the proposal includes a requirement whereby Manufacturers are required to inform their relevant competent authority and health institutions if there is a temporary, or permanent interruption in the supply of their IVDs, especially if there are few or no alternative products, or where there is a risk of serious harm to patients or public health.
How will this impact industry readiness to IVDR?
The proposal offers a short term solutions for the current state of readiness in the industry for IVDR, especially for Class D devices, which often include low volume, but highly critical diagnostics which were at risk of not meeting IVDR compliance before the deadline of May 2025.
The proposal also encourages an increased usage of Eudamed, which has seen low adoption (caused in part by the delays to each module) by manufacturers within the UDI and Devices module.
In a wider sense, the commission is trying to mitigate the risk of supply shortages as a result of the IVDR transition, although it is currently up to the manufacturer to determine the severity of risk to supply for their products.
Don’t delay
The proposal allows a collective sigh of relief, allowing the industry more time to prepare the technical documentation and engage with a notified body. However in reality, the additional timelines do not offer time to pause. The additional 2 year delay allows the completion of the conformity assessment process, it does not provide any further time for getting the QMS ready for the IVDR. The amendment also allows manufacturers to also ensure their clinical evidence is compliant as we know that legacy devices require additional performance testing before they are IVDR compliant.
In the long term it remains to be seen how significant this amendment will elevate the challenges facing the industry as they transition from IVDD to IVDR. It remains to be seen to what extent the industry will be ready in another 2 years time.
While this should be seen as a positive, we would encourage Manufacturers to press forward with their IVDR transition planning now. For more information on how IVDeology have supported our customers achieve IVDR compliance, contact [email protected].
Note: This blog contains a summary of the key changes within the proposal, it is important that Manufacturers read and understood the proposal in full, and get independent legal advice if required.